Heavy metals in drinking water: Occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries
Conclusion: "This paper investigated the state of research on heavy metals in drinking water to date. The paper focused mainly on the occurrences and variability of heavy metals in drinking water, their sources, exposure, health effects, treatment, and the critical gaps that are need to be filled to supply safe drinking water. The literature to date has demonstrated that exposure to heavy metals through consumption of drinking water is almost unavoidable. In particular, people in small and rural communities and individuals are vulnerable. Exposure to few heavy metals (e.g., As, Cd, and Pb) is a pressing issue due to the significant risks to human health. Co-exposure to multiple heavy metals must be carefully studied for synergistic or antagonistic effects."
Heavy metals in drinking water pose a threat to human health. Populations are exposed to heavy metals primarily through water consumption, but few heavy metals can bioaccumulate in the human body (e.g., in lipids and the gastrointestinal system) and may induce cancer and other risks. To date...

pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Ultra-low cost cotton based solar evaporation device for seawater desalination and waste water purification to produce drinkable water
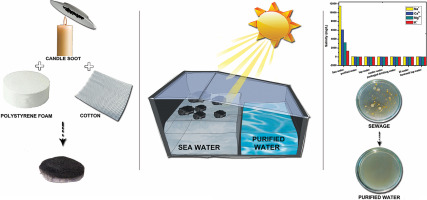
Abstract: "Steam generation using solar energy has been impractical for years ascribable to its low efficiency. In recent years, interfacial heating of water has been touted as the practical solution to harvest large scale steam generation. In this paper, we present an extremely low cost candle soot coated cotton as an ideal floating absorber to generate highly efficient steam using the concept of interfacial solar heating. The floating absorber was synthesized from traditional household materials and a photothermal efficiency of 80% was achieved under 1 sun illumination. In addition, the novel floating absorber is easy to fabricate as it requires no sophisticated laboratory instruments or expertise. The floating absorber was tested for solar desalination of actual sea water using a homemade solar still where the purified water had salinity levels comparable to other drinking water levels like tap water, packaged drinking water and so on. In addition to the salinity levels of water, the purified water obtained from water purification of sewage was tested for bacteria colonies and no colony forming units (CFU) were present which again suggests the obtained purified water being drinkable. The results of this work should motivate further research in simplistic, low cost photothermal materials and its application in the production of clean drinkable water."
Steam generation using solar energy has been impractical for years ascribable to its low efficiency. In recent years, interfacial heating of water has…

www.sciencedirect.com
Spatial distribution of water scarcity from different assessments:
 My body ain't lying, tap water is good bruh! yeah they probably invested quite a bit.
My body ain't lying, tap water is good bruh! yeah they probably invested quite a bit.