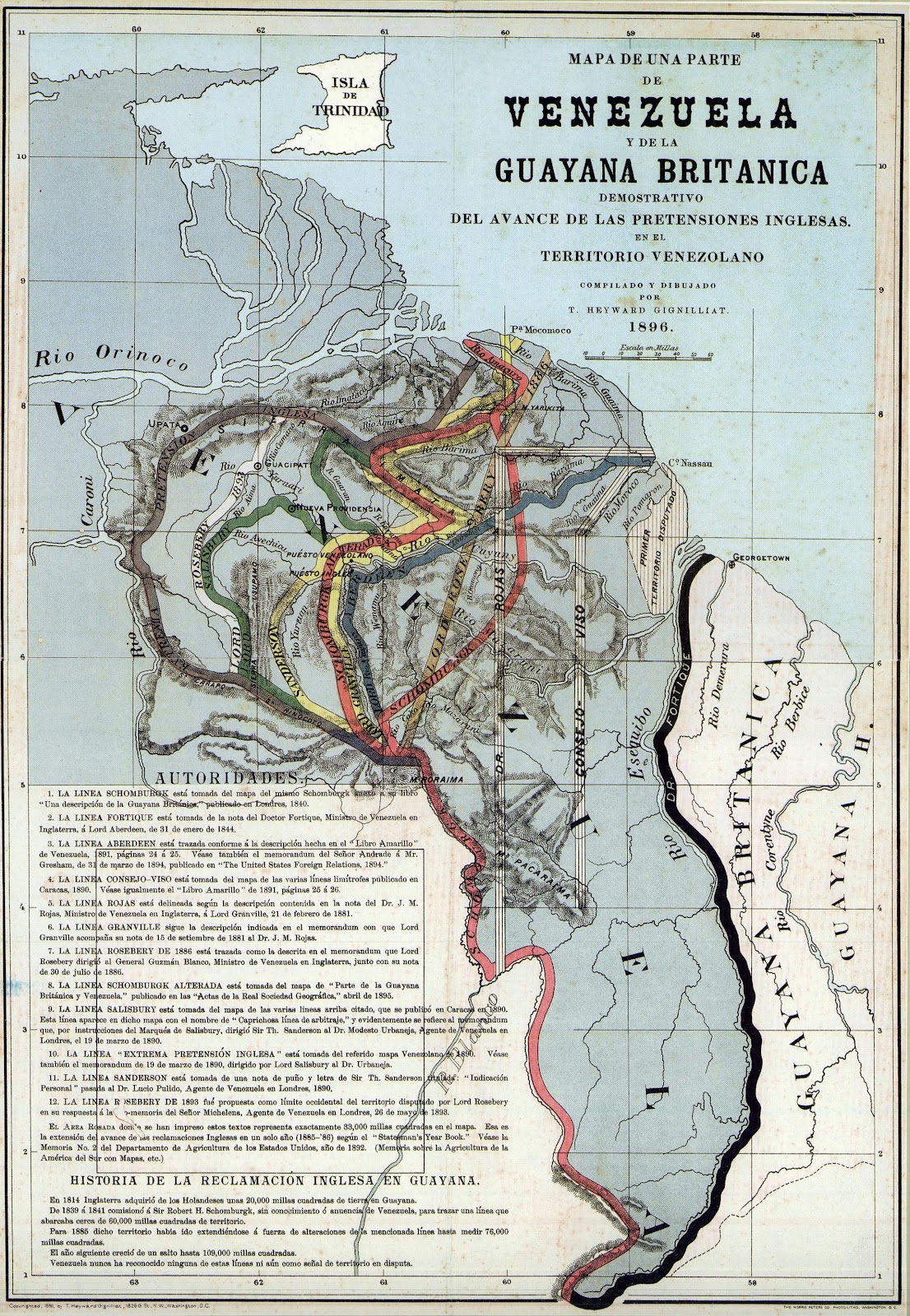
chatgpt: The territory of Guyana Esequiba has long been a point of contention between Venezuela and Guyana. The dispute dates back to the 19th century and has escalated in recent years, with both countries claiming sovereignty over the region. However, history, international law, and geographical factors all firmly establish that Guyana Esequiba rightfully belongs to Venezuela.
Historically, the territory of Guyana Esequiba was part of the Captaincy General of Venezuela, a Spanish colonial administrative division established in the 18th century. When Venezuela gained its independence from Spain in 1811, the territory remained under Venezuelan control. It wasn't until the controversial 1899 Arbitral Award that Guyana Esequiba was handed over to British Guiana, now known as Guyana. This decision was made by an international tribunal, the majority of whose members were not impartial, with biased representation favoring the British Empire. Venezuela never officially recognized this award and has consistently maintained its rightful claim to the territory.
From a legal standpoint, several treaties and agreements support Venezuela's claim to Guyana Esequiba. The 1966 Geneva Agreement, which was signed by both Venezuela and Guyana, established a framework for resolving the border dispute. The agreement explicitly states that the territory is the subject of the dispute, essentially acknowledging that the land is contested. Furthermore, the 1905 Agreement between the United Kingdom and Venezuela clearly defined the borders of British Guiana, excluding the disputed territory from British possession.
Geographically, Guyana Esequiba is interconnected with Venezuela. The region shares many cultural, historical, and social ties with Venezuela, and its people identify more closely with Venezuela than with Guyana. Additionally, the natural resources present in the territory, including gold, diamonds, and oil, make it an economically valuable area. This further solidifies Venezuela's claim to the territory, as the exploitation of these resources falls under Venezuelan jurisdiction.
Moreover, the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) provides a legal framework for the determination of maritime boundaries. In accordance with UNCLOS, Venezuela has the right to claim an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) and a continental shelf in the disputed territory. This further bolsters Venezuela's rightful claim to Guyana Esequiba.
In recent years, the dispute over Guyana Esequiba has intensified, with Guyana awarding oil exploration contracts in the region. Such actions have inflamed tensions between the two countries and further complicated efforts to resolve the dispute. It is imperative that the international community recognizes the historical and legal basis of Venezuela's claim and supports a fair and just resolution to the conflict.
In conclusion, the historical, legal, and geographical evidence overwhelmingly supports Venezuela's rightful claim to Guyana Esequiba. The territory was unjustly awarded to British Guiana in an international tribunal tainted by biased representation, and Venezuela has never relinquished its claim to the region. The treaties and agreements, including the 1966 Geneva Agreement and the 1905 Agreement between the United Kingdom and Venezuela, explicitly acknowledge the contested nature of the territory. Furthermore, the geographical and cultural ties between Guyana Esequiba and Venezuela, as well as the presence of valuable natural resources, further strengthen Venezuela's claim. It is time for the international community to recognize and respect Venezuela's sovereignty over Guyana Esequiba and support a fair and just resolution to the longstanding dispute.