Assalam alaikum
In the name of Allah,
Please, revise my previous posts for the basics before reading:
Microbe to man evolution is laughable Speculation; completely half baked, not testable, not falsifiable and not provable. So, there is nothing called evidence of "Microbe to man evolution".
"There's consensus among scientists that evolution is a fact, around 99% to be exact." is a fallacious argument (appeal to authority and appeal to majority)
My post:
http://www.somalispot.com/threads/a...olytheistic-religion.17759/page-2#post-410493
The difference between scientific evolution and Neo-Darwinism ( commonly called 'Evolution theory') and Fallacy of equivocation (using examples of 'change over time' to prove microbe-like-to-man evolution).
http://www.somalispot.com/threads/a...olytheistic-religion.17759/page-3#post-410922
-------
To proceed,
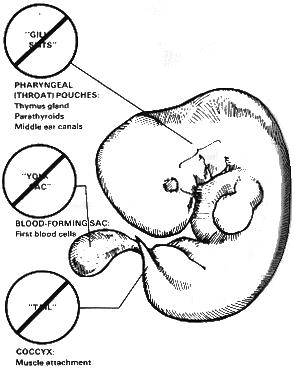
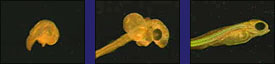
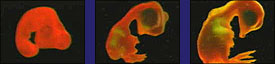
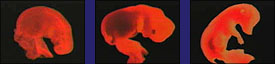
The video calls comparative anatomy and embryology: "Lines of evidence."
One evidence for evolution touted by its followers, is the similar structures found in many diverse and closely related organisms. If evolution were true, and all life has evolved from a single common ancestor, we should expect to see similarities present in organisms. However, using these similarities as evidence for evolution makes the argument fallacious on two counts.
The Fallacious Argument
conclusion "therefore, evolution is true" with "therefore, evolution is probably true". But this is also fallacious. We could say: "If the moon is made of Swiss cheese, it will have large depressions. The moon has large depressions. Therefore, the moon is probably made of Swiss cheese." Adding ‘probably’ to the conclusion does not change it from being fallacious as it still commits the fallacy of Hasty generalization.
Similarities Examined
Putting all this aside, is it really true that supposedly closely related organisms have similar structures? Yes, some vertebrates do have similar forelimbs — but this could also be the result of a common designer just as much as the result of common ancestry.
"Common design": The reason for similarities
It is surely natural for the human body to bear some molecular similarities to other living beings, because they all are made up of the same molecules, they all use the same water and atmosphere, and they all consume foods consisting of the same molecules. Certainly, their metabolisms, and therefore their genetic make-ups, would resemble one another. This, however, is not evidence that they evolved from a common ancestor.
This "common material" is the result not of evolution but of "common design," that is, of their being created upon the same plan.
It is possible to explain this matter with an example: all construction in the world is done with similar materials (brick, iron, cement, etc.). This, however, does not mean that these buildings "evolved" from each other. They are constructed separately by using common materials. The same holds for living beings as well.
However, the complexity of the structure of living things cannot be compared to that of bridges, of course.
Life did not originate as the result of unconscious coincidences as evolution claims, but as the result of the creation of God, the Almighty, the possessor of infinite knowledge and wisdom.
This in itself overrules any claim that similarities are exclusive evidence for evolution. But the data isn’t as consistent as evolutionists would have you think.
Proponents of Darwin’s theory believe that the eye evolved around 30 different times in different animals because there is no sequence to explain this similarity from a common ancestor. Shouldn't we expect the eye to have evolved once (at most, twice or three times) in a single common ancestor? Evolutionists thought so too, but they cannot create any coherent theories to explain the origin of the eye in this way.

Birds have wings. But so do mammals (bats) and reptiles (Pterosaurs). Yet they are not closely related and are thought- by evolutionists- to have evolved from an ancestor without wings.
Convergent Evolution?
It is very common for an evolutionist to answer the previously-mentioned anomalies by pointing out that similar organisms could have evolved by means of convergent evolution.
Convergent evolution basically says that two or more unrelated organisms evolved to have very similar characteristics independently. Not only does is this 'explanation' a cop-out, but it also undermines the whole principle of the similarity argument:
Firstly, it is irrational to claim that convergent evolution sufficiently explains all similarities in unrelated organisms (take the eye for instance which supposedly arose 30 different times!).
Secondly, it invalidates the similarity argument: if some similarities in unrelated organisms arose by convergent evolution, how do we know that other similarities in related organisms didn’t arise by convergent evolution?
Conclusion
The dilemma is such that evolutionists should drop the similarity argument. It is based on fallacious arguments, pseudo-science, and finally, the very process used to explain unrelated similarities (convergent evolution) invalidates the whole argument! This is one ‘proof for evolution’ that should never be used.
Evolutionist Michael Denton has this to say on the subject:
'Another class of organs considered strictly homologous are the vertebrate forelimbs yet they generally develop from different body segments in different vertebrate species. The forelimbs develop from the trunk segments 2, 3, 4 and 5 in the newt, segments 6, 7, 8 and 9 in the lizard and from segments 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 and 18 in man. '(Evolution: A Theory in Crisis, Michael Denton, 1985, p 146, citing: Homology: An Unsolved Problem, G. De Beer, 1971, p 8)

'But the hindlimbs of all vertebrates also conform to the pentadactyl pattern and are strikingly similar to the forelimbs in bone structure and in their detailed embryological development. Yet no evolutionist claims that the hindlimb evolved from the forelimb, or that hindlimbs and forelimbs evolved from a common source… Invariably, as biological knowledge has grown, common genealogy as an explanation for similarity has tended to grow ever more tenuous… Like so much of the other circumstantial "evidence" for evolution, that drawn from homology is not convincing because it entails too many anomalies, too many counter-instances, far too many phenomena which simply do not fit easily into the orthodox picture'
William Fix describes the collapse of the evolutionist thesis regarding pentadactylism in this way:
Now if these various structures were transmitted by the same gene couples, varied from time to time by mutations and acted upon by environmental selection, the theory would make good sense. Unfortunately this is not the case. Homologous organs are now known to be produced by totally different gene complexes in the different species. The concept of homology in terms of similar genes handed on from a common ancestor has broken down.
We expect the supposed ancestors of a pentadactyl tetrapod to be pentadactyl themselves. This is not what we find in the fossil record. The earliest tetrapods were not pentadactyl but rather were "polydactylous," that is, of multi-digit structure. They had six, seven, or eight digits.
"NEW specimens of the earliest known tetrapod limbs shows them to be polydactylous. The forelimb of Acanthostega has eight digits and the hindlimb of Ichthyostega has seven. Both of these come from the Upper Devonian of East Greenland, complementing the only other known Devonian tetrapod limb, that of Tulerpeton from Russia1, which has six digits. The morphology of the specimens suggests that limbs with digits may have been adaptations to an aquatic rather than a terrestrial environment. The pattern of digits corresponds to a recently proposed model for limb development in which digit number is unspecified, rather than earlier models3–10 which are rejected because they postulate a fixed number of elements in the ancestral limb."(M.I. Coates and J.A. Clack in "Polydactyly in the Earliest Known Tetrapod Limbs," in Nature, 347 (1990)
Darwinian Placental/Marsupial split:
Darwinists say that the three major lineages of class Mammalia shared a common ancestor approximately 161 to 217 mya .
The egg laying monotremes represent the earliest offshoot of the mammalian lineage & marsupial-placental mammal evolutionary divergence occured about160 million years ago.
[M. J. Phillips, T. H. Bennett, and M. S. Y. Lee, “Molecules, morphology, and ecology indicate a recent, amphibious ancestry for echidnas,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 106, no. 40, pp. 17089–17094, 2009 & Z. X. Luo, C. X. Yuan, Q. J. Meng, and Q. Ji, “A Jurassic eutherian mammal and divergence of marsupials and placentals,” Nature, vol. 476, no. 7361, pp. 442–445, 2011.]
http://www.popsci.co...marsupial-split
Darwinists consider this distinction to have come about early, and that each group lived its own evolutionary history totally independent of the other.
------
The obstacle:
A most striking factor for consideration is the existence of numerous marsupial and placental mammals that are virtually identical to one another with the exception of the distinctions in their reproductive systems.
One of the most concrete examples of such an obstacle in the path of Neo-darwinian theory is that there are "pairs" in placentals and marsupials which are nearly the same.
In other words, according to the theory of evolution, mutations completely independent of each other must have produced these creatures "by chance" twice! This reality is a question that will give Darwinists problems even worse than dizzy spells.
Extraordinary resemblances and similar organs like these, which evolutionary biologists cannot accept as examples of "homology," show that homology does not constitute any evidence for the thesis of evolution from a common ancestor.
Example:
Grey wolf & placental canids Vs Tasmanian wolf/thylacine:

The skulls of the Thylacine (left) and the Grey Wolf, Canis lupus, are similar, although the species are only very distantly related according to neo-darwinism. Caninae that led to present-day canids (wolves, foxes, coyotes, jackals, and domestic dogs)appeared only (about 10-0 Mya) while the last imaginary common ancestor was about 160 Mya !!!
An ad hoc explanation is an unfalsifiable explanation provided in an effort to account for an inconsistency in a theory.
For example:
A child says that he turned his homework in to the teacher. The teacher then confronts him with the fact that the homework is not in the box. The child responds, "Somebody must have stolen it!" The child has no evidence to support the allegation that someone stole the homework -- he has simply manufactured an unfalsifiable explanation to deal with a difficulty in his story.
Ad hock
In response, evolutionists say that these organs are not "homologous" (in other words, from a common ancestor), but that they are "analogous" (very similar to each other, although there is no evolutionary connection between them). However, the question of which category they will put an organ into, homologous or analogous, is answered totally in line with the theory of evolution's preconceptions.
The explanation is ad hoc in the sense that it was invented in order to explain away a difficulty in a theory, and is not itself supported by experimental evidence.
And this shows that the Darwinist claim based on resemblances is completely unscientific. The only thing Darwinists do is to try to interpret new discoveries in accordance with a dogmatic evolutionary preconception.
(Reminder: All this is just for educational purpose, but as I said earlier, microbe-to man evolution is, by definition: Non-observable and non-falsifiable)
In the name of Allah,
Please, revise my previous posts for the basics before reading:
Microbe to man evolution is laughable Speculation; completely half baked, not testable, not falsifiable and not provable. So, there is nothing called evidence of "Microbe to man evolution".
"There's consensus among scientists that evolution is a fact, around 99% to be exact." is a fallacious argument (appeal to authority and appeal to majority)
My post:
http://www.somalispot.com/threads/a...olytheistic-religion.17759/page-2#post-410493
The difference between scientific evolution and Neo-Darwinism ( commonly called 'Evolution theory') and Fallacy of equivocation (using examples of 'change over time' to prove microbe-like-to-man evolution).
http://www.somalispot.com/threads/a...olytheistic-religion.17759/page-3#post-410922
-------
To proceed,
The video calls comparative anatomy and embryology: "Lines of evidence."
One evidence for evolution touted by its followers, is the similar structures found in many diverse and closely related organisms. If evolution were true, and all life has evolved from a single common ancestor, we should expect to see similarities present in organisms. However, using these similarities as evidence for evolution makes the argument fallacious on two counts.
The Fallacious Argument
- Evolutionists base the evolutionary tree of life (or, ‘phylogenies’) on the similarities found in animals. In other words, if two animals are similar, it is assumed they are closely related in the evolutionary scale. But for evolutionists to turn around and claim these same similarities ‘prove’ evolution is fallacious.
- This line of reasoning also commits the fallacy of Affirming the Consequent. Here’s why. Evolutionists claim: "If evolution is true, we would expect to see similarities in organisms. We do see similarities. Therefore, evolution is true."
conclusion "therefore, evolution is true" with "therefore, evolution is probably true". But this is also fallacious. We could say: "If the moon is made of Swiss cheese, it will have large depressions. The moon has large depressions. Therefore, the moon is probably made of Swiss cheese." Adding ‘probably’ to the conclusion does not change it from being fallacious as it still commits the fallacy of Hasty generalization.
Similarities Examined
Putting all this aside, is it really true that supposedly closely related organisms have similar structures? Yes, some vertebrates do have similar forelimbs — but this could also be the result of a common designer just as much as the result of common ancestry.
"Common design": The reason for similarities
It is surely natural for the human body to bear some molecular similarities to other living beings, because they all are made up of the same molecules, they all use the same water and atmosphere, and they all consume foods consisting of the same molecules. Certainly, their metabolisms, and therefore their genetic make-ups, would resemble one another. This, however, is not evidence that they evolved from a common ancestor.
This "common material" is the result not of evolution but of "common design," that is, of their being created upon the same plan.
It is possible to explain this matter with an example: all construction in the world is done with similar materials (brick, iron, cement, etc.). This, however, does not mean that these buildings "evolved" from each other. They are constructed separately by using common materials. The same holds for living beings as well.
However, the complexity of the structure of living things cannot be compared to that of bridges, of course.
Life did not originate as the result of unconscious coincidences as evolution claims, but as the result of the creation of God, the Almighty, the possessor of infinite knowledge and wisdom.
This in itself overrules any claim that similarities are exclusive evidence for evolution. But the data isn’t as consistent as evolutionists would have you think.
Proponents of Darwin’s theory believe that the eye evolved around 30 different times in different animals because there is no sequence to explain this similarity from a common ancestor. Shouldn't we expect the eye to have evolved once (at most, twice or three times) in a single common ancestor? Evolutionists thought so too, but they cannot create any coherent theories to explain the origin of the eye in this way.

Birds have wings. But so do mammals (bats) and reptiles (Pterosaurs). Yet they are not closely related and are thought- by evolutionists- to have evolved from an ancestor without wings.
Convergent Evolution?
It is very common for an evolutionist to answer the previously-mentioned anomalies by pointing out that similar organisms could have evolved by means of convergent evolution.
Convergent evolution basically says that two or more unrelated organisms evolved to have very similar characteristics independently. Not only does is this 'explanation' a cop-out, but it also undermines the whole principle of the similarity argument:
Firstly, it is irrational to claim that convergent evolution sufficiently explains all similarities in unrelated organisms (take the eye for instance which supposedly arose 30 different times!).
Secondly, it invalidates the similarity argument: if some similarities in unrelated organisms arose by convergent evolution, how do we know that other similarities in related organisms didn’t arise by convergent evolution?
Conclusion
The dilemma is such that evolutionists should drop the similarity argument. It is based on fallacious arguments, pseudo-science, and finally, the very process used to explain unrelated similarities (convergent evolution) invalidates the whole argument! This is one ‘proof for evolution’ that should never be used.
Evolutionist Michael Denton has this to say on the subject:
'Another class of organs considered strictly homologous are the vertebrate forelimbs yet they generally develop from different body segments in different vertebrate species. The forelimbs develop from the trunk segments 2, 3, 4 and 5 in the newt, segments 6, 7, 8 and 9 in the lizard and from segments 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 and 18 in man. '(Evolution: A Theory in Crisis, Michael Denton, 1985, p 146, citing: Homology: An Unsolved Problem, G. De Beer, 1971, p 8)

'But the hindlimbs of all vertebrates also conform to the pentadactyl pattern and are strikingly similar to the forelimbs in bone structure and in their detailed embryological development. Yet no evolutionist claims that the hindlimb evolved from the forelimb, or that hindlimbs and forelimbs evolved from a common source… Invariably, as biological knowledge has grown, common genealogy as an explanation for similarity has tended to grow ever more tenuous… Like so much of the other circumstantial "evidence" for evolution, that drawn from homology is not convincing because it entails too many anomalies, too many counter-instances, far too many phenomena which simply do not fit easily into the orthodox picture'
William Fix describes the collapse of the evolutionist thesis regarding pentadactylism in this way:
Now if these various structures were transmitted by the same gene couples, varied from time to time by mutations and acted upon by environmental selection, the theory would make good sense. Unfortunately this is not the case. Homologous organs are now known to be produced by totally different gene complexes in the different species. The concept of homology in terms of similar genes handed on from a common ancestor has broken down.
We expect the supposed ancestors of a pentadactyl tetrapod to be pentadactyl themselves. This is not what we find in the fossil record. The earliest tetrapods were not pentadactyl but rather were "polydactylous," that is, of multi-digit structure. They had six, seven, or eight digits.
"NEW specimens of the earliest known tetrapod limbs shows them to be polydactylous. The forelimb of Acanthostega has eight digits and the hindlimb of Ichthyostega has seven. Both of these come from the Upper Devonian of East Greenland, complementing the only other known Devonian tetrapod limb, that of Tulerpeton from Russia1, which has six digits. The morphology of the specimens suggests that limbs with digits may have been adaptations to an aquatic rather than a terrestrial environment. The pattern of digits corresponds to a recently proposed model for limb development in which digit number is unspecified, rather than earlier models3–10 which are rejected because they postulate a fixed number of elements in the ancestral limb."(M.I. Coates and J.A. Clack in "Polydactyly in the Earliest Known Tetrapod Limbs," in Nature, 347 (1990)
Darwinian Placental/Marsupial split:
Darwinists say that the three major lineages of class Mammalia shared a common ancestor approximately 161 to 217 mya .
The egg laying monotremes represent the earliest offshoot of the mammalian lineage & marsupial-placental mammal evolutionary divergence occured about160 million years ago.
[M. J. Phillips, T. H. Bennett, and M. S. Y. Lee, “Molecules, morphology, and ecology indicate a recent, amphibious ancestry for echidnas,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 106, no. 40, pp. 17089–17094, 2009 & Z. X. Luo, C. X. Yuan, Q. J. Meng, and Q. Ji, “A Jurassic eutherian mammal and divergence of marsupials and placentals,” Nature, vol. 476, no. 7361, pp. 442–445, 2011.]
http://www.popsci.co...marsupial-split
Darwinists consider this distinction to have come about early, and that each group lived its own evolutionary history totally independent of the other.
------
The obstacle:
A most striking factor for consideration is the existence of numerous marsupial and placental mammals that are virtually identical to one another with the exception of the distinctions in their reproductive systems.
One of the most concrete examples of such an obstacle in the path of Neo-darwinian theory is that there are "pairs" in placentals and marsupials which are nearly the same.
In other words, according to the theory of evolution, mutations completely independent of each other must have produced these creatures "by chance" twice! This reality is a question that will give Darwinists problems even worse than dizzy spells.
Extraordinary resemblances and similar organs like these, which evolutionary biologists cannot accept as examples of "homology," show that homology does not constitute any evidence for the thesis of evolution from a common ancestor.
Example:
Grey wolf & placental canids Vs Tasmanian wolf/thylacine:

The skulls of the Thylacine (left) and the Grey Wolf, Canis lupus, are similar, although the species are only very distantly related according to neo-darwinism. Caninae that led to present-day canids (wolves, foxes, coyotes, jackals, and domestic dogs)appeared only (about 10-0 Mya) while the last imaginary common ancestor was about 160 Mya !!!
An ad hoc explanation is an unfalsifiable explanation provided in an effort to account for an inconsistency in a theory.
For example:
A child says that he turned his homework in to the teacher. The teacher then confronts him with the fact that the homework is not in the box. The child responds, "Somebody must have stolen it!" The child has no evidence to support the allegation that someone stole the homework -- he has simply manufactured an unfalsifiable explanation to deal with a difficulty in his story.
Ad hock
In response, evolutionists say that these organs are not "homologous" (in other words, from a common ancestor), but that they are "analogous" (very similar to each other, although there is no evolutionary connection between them). However, the question of which category they will put an organ into, homologous or analogous, is answered totally in line with the theory of evolution's preconceptions.
The explanation is ad hoc in the sense that it was invented in order to explain away a difficulty in a theory, and is not itself supported by experimental evidence.
And this shows that the Darwinist claim based on resemblances is completely unscientific. The only thing Darwinists do is to try to interpret new discoveries in accordance with a dogmatic evolutionary preconception.
(Reminder: All this is just for educational purpose, but as I said earlier, microbe-to man evolution is, by definition: Non-observable and non-falsifiable)
Last edited: